Computing size integrals
Jaideep Joshi
11 March 2022
size_integral_dev.RmdDeveloper notes for computing the size integral
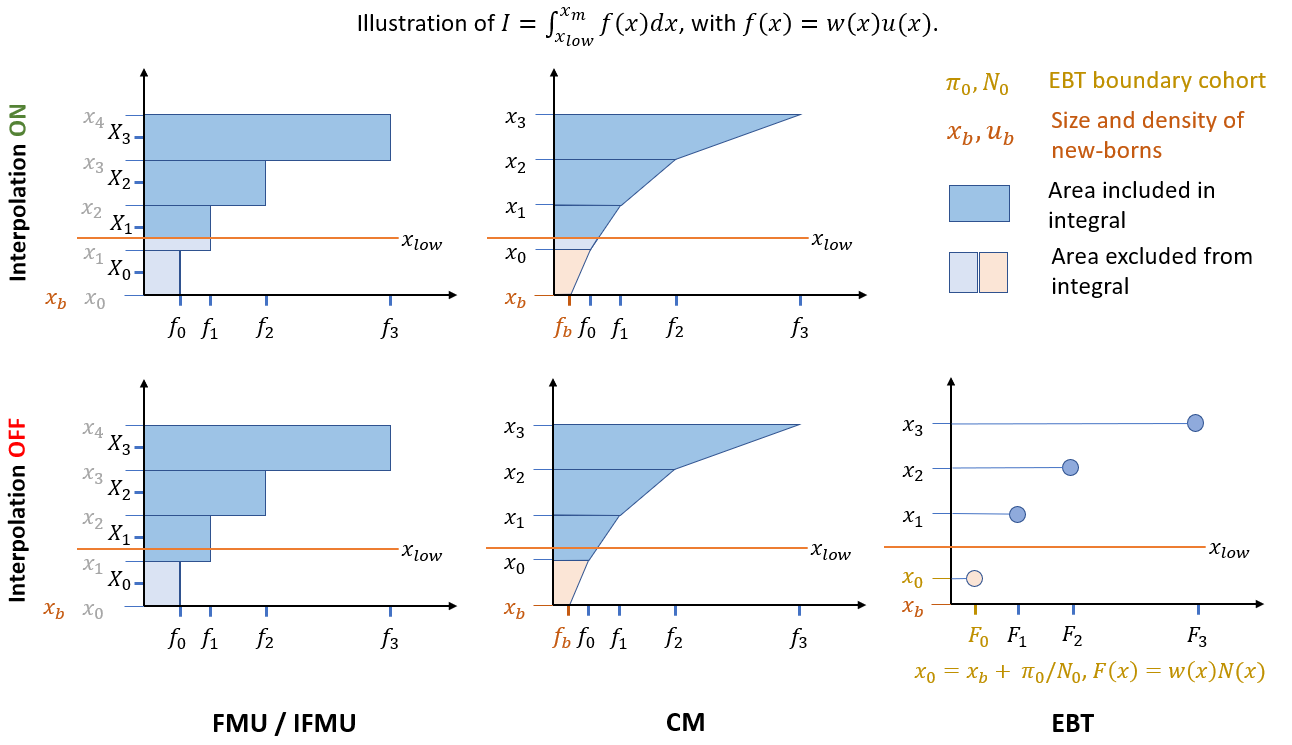
In libpspm, the computation of this integral depends on the solver method. For different solvers, the integral is defined as follows:
FMU: \(\quad I =
\sum_{i=i_0}^J h_i w_i u_i\)
EBT: \(\quad I =
\sum_{i=i_0}^J w_i N_i\), with \(x_0 =
x_b + \pi_0/N_0\)
CM : \(\quad I =
\sum_{i=i_0}^J h_i (w_{i+1}u_{i+1}+w_i u_i)/2\)
where \(i_0 = \text{argmax}(x_i \le x_{low})\), \(h_i = x_{i+1}-x_i\), and \(w_i = w(x_i)\).
If interpolation is turned on, \(h_{i_0}=x_{i_0+1}-x_{low}\), whereas \(u(x_{low})\) is set to \(u(x_{i_0})\) in FMU and calculated by bilinear interpolation in CM (See Figure). Interpolation does not play a role in EBT.
In the CM method, the density of the boundary cohort is obtained from the boundary condition of the PDE: \(u_b=B/g(x_b)\), where \(B\) is the input flux of newborns. In the current implementation of the CM method, \(B\) must be set to a constant. In future implementations which may allow real-time calculation of \(B\), \(u_b\) must be calculated recurvisely by solving \(u_b = B(u_b)/g(x_b)\), where \(B(u_b) = \int_{x_b}^{x_m} f(x)u(x)dx\).